7 key factors that influence foreign exchange rates

This article covers:
If there’s one thing that can make a traveller or expat break out in a cold sweat, it’s those dreaded exchange rates. You could save up a lifetime of cash and still end up feeling like you’ve been duped by those sneaky little numbers. But fear not my friends, for we are here to guide you through this confusing world of currency.
In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know about exchange rates and even throw in 7 factors affecting foreign exchange rates. So sit back, relax, and get ready to exchange those dollars for some pesos, euros or yen like a pro.
What controls the exchange rate?
Exchange rates can be like a rollercoaster ride – thrilling at times, nauseating at others. But they’re more than just a number on a screen or in the news. Think of them as prices, some are consistent like your favourite coffee shop’s latte, while others are unpredictable like the weather.
There are two types of exchange rates – fixed and floating.
Back in the day, fixed exchange rates used gold and silver to set the value, but now it’s a managed floating exchange rate. Floating exchange rates are influenced by what governments and banks do.
What is an example of an exchange rate?
Exchange rates are simply the value of one currency in comparison to another. Example: USD to INR.
What is the importance of exchange rates?
Why do we need to care about exchange rates, you ask? Well, aside from the fact that they make economists feel important, exchange rates can tell us a lot about a country’s economic well-being. It’s like checking your bank account balance, but for an entire nation (and without the crippling anxiety). Essentially, exchange rates determine how much one country’s currency is worth in comparison to another’s. This impacts everything from import-export balances to foreign investment opportunities.
How do exchange rates affect the economy?
Well, well, well, looks like our little friend “exchange rate” is at it again, affecting the real economy like it’s the boss of the world. But let’s be real, the most direct impact it has is on the demand for exports and imports.
When the domestic currency depreciates, exports become more desirable to foreign buyers because they’re cheaper (smart move, currency). But, it also makes imports more expensive, making us feel like we’re broke college students trying to buy top-shelf liquor at the bar.
The good news? Domestic goods are suddenly hot commodities themselves, giving a much-needed boost to our economy.
What happens when exchange rates increase?
Well, it’s like you suddenly got a raise and everything became a little bit cheaper. Trading with other countries just got a whole lot more interesting.
You can now buy more fancy French cheese for the same amount of money you used to spend on domestic cheddar (sacre bleu!). And don’t even get me started on the potential for cheaper vacations abroad. Suddenly, those overpriced cocktails on the beach don’t seem so overpriced anymore.
Of course, the downside is that our own exports become less attractive to foreign buyers, so it’s a bit of a double-edged sword.
7 factors affecting exchange rates
Here’s the deal – these rates can be affected by a whole lot of factors, and no, we’re not talking about mystical forces or ancient spells (although that would make it way more interesting). We’ll cover the basics in a way that even your grandma could understand!
1. Interest and inflation rates
Inflation is the rate at which the cost of goods and services rises over time. Interest rates indicate the amount charged by banks for borrowing money. These two are linked by the fact that people tend to borrow and spend more when the interest rates are low, which results in an increase in costs. These rates are direct indicators of the current and future economic performance of a country and can influence the decisions of forex investors and traders throughout the globe. An increase in interest rate is usually followed by a rise in the value of the local currency.
This happens usually because the economy is growing too fast and central banks are trying to slow inflation.
2. Current account deficits
The current account is the balance of trade between a country and its trading partners. It describes the difference in value between the goods and services traded with other countries. If a country buys more than it sells then the balance of trade is a deficit. It directly affects the exchange rate since a country will need more foreign capital, thus diminishing the demand for local currency. This excess supply of local currency drives down its value against foreign currency.
You might also like to read: Foreign transaction fee in overseas spending: what does it mean to consumer
3. Government debt
This is the total national or public debt owed by the central government. A country with a large amount of government debt is less likely to attract foreign investment and acquire foreign capital, leading to inflation. It may also happen that existing foreign investors will sell their bonds in the open market if they foresee an increase in government debts. This will result in an oversupply of the local currency, thus diminishing its value.
4. Terms of trade
Terms of trade are the ratio of the export prices of a country to its import prices. When the export prices of a country rise at a greater rate than its import prices, its terms of trade improves. This in turn results in higher revenue, higher demand for the country’s currency, and an increase in the value of the currency. This cumulatively results in appreciation of the exchange rate of the currency.
5. Economic performance
One of the many factors that affect the economic performance of a country is its political stability. A country, which has a stable political environment, attracts more foreign investment and vice versa. An increase in foreign capital results in appreciation in the value of its domestic currency. Such stability also directly affects the financial and trade policy, thus eliminating any uncertainty in the value of its currency.
You might also like to read: Best places to exchange currency while travelling abroad
6. Recession
During a recession, a country’s interest rates are likely to fall, thus decreasing its chances to acquire foreign capital. This in turn weakens the currency of the country in question, weakening the exchange rate.
7. Speculation
Investors demand more of a country’s currency when its value is expected to rise to make a profit in the near future. As a result, the value of the currency rises due to its increased demand. Which in turn results in a rise in the exchange rate as well.
With so many factors involved, exchange rates are subject to fluctuations and that can be pretty distressing for people who transfer money overseas frequently. Though watching the rates of a currency corridor can give you a fair idea of the best time to make transfers, it’s best to stay updated about the real-time exchange rates.
How Instarem can help you with exchange rates?
If you’re a globetrotter who loves to explore the world, you may already be familiar with exchange rate hassles. Unless you’ve been living under a rock, you know that traditional methods of transferring money between borders often come with unfair rates, incomprehensible fees, and other complications.
But don’t worry! Instarem has got your back.
With our ground-breaking service, we can offer you a smarter, faster and more affordable way to send money overseas.
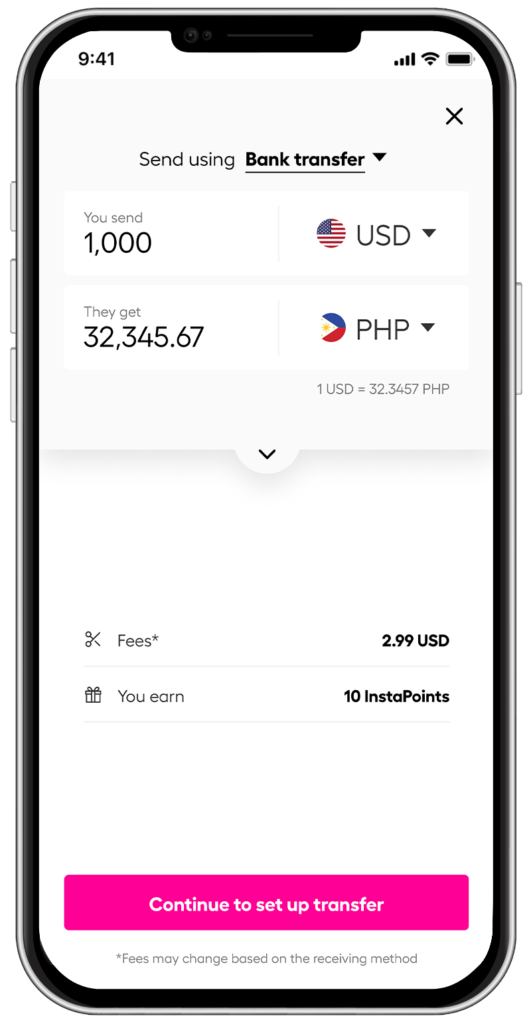
*rates are for illustration purpose only.
So there’s no need to worry about hidden costs or unfair exchange rates when sending money across 60+ countries- Instarem has taken all the guesswork out of it. Ready to transfer money abroad?
 Get the app
Get the app


























